In 2015 my post “5 Things you need to know about PSD2” was pretty popular and was widely shared. Since then i have written other PSD2 related posts from 2FA, infographics through to bank readiness to adopt and adhere to the European open banking regulation. In this post, given that Open Banking was 1 year old in January 2019 i thought i would summarise some of the best PSD2 graphics since they nicely and simply capture what we need to know.
Traditional Banking versus Open Banking
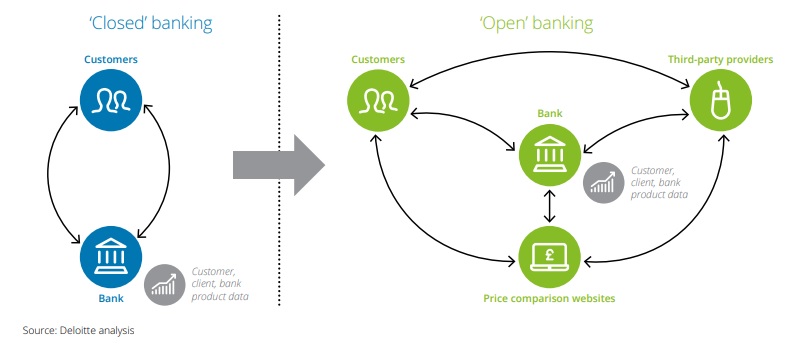
Before we go any further, know that there will be references to Open Banking. PSD2 is the European adoption of Open Banking. From the Deloitte whitepaper on Open Banking, this graphic nicely captures the difference between the old days and Open Banking. The customer has the choice to choose where they wish to enable their banking:
Ref: How to flourish in an uncertain future | Deloitte
In a nutshell, PSD2….
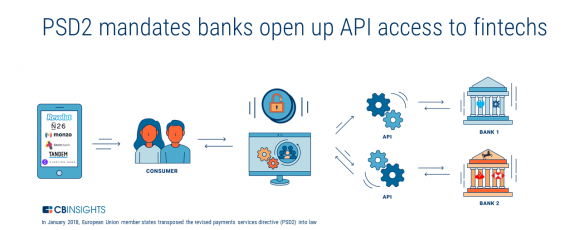
The CB Insights posts about banking nicely explains the purpose of PSD2 and Open Banking – i.e. allowing challengers in the financial services space to grow and plug into the ol’ banking network. Let’s get into a bit more detail…
Ref: The Challenger Bank Playbook: How 6 Digital Banking Startups Are Taking On Retail Banking | CB Insights
PSD2 Explained – European Payments Council
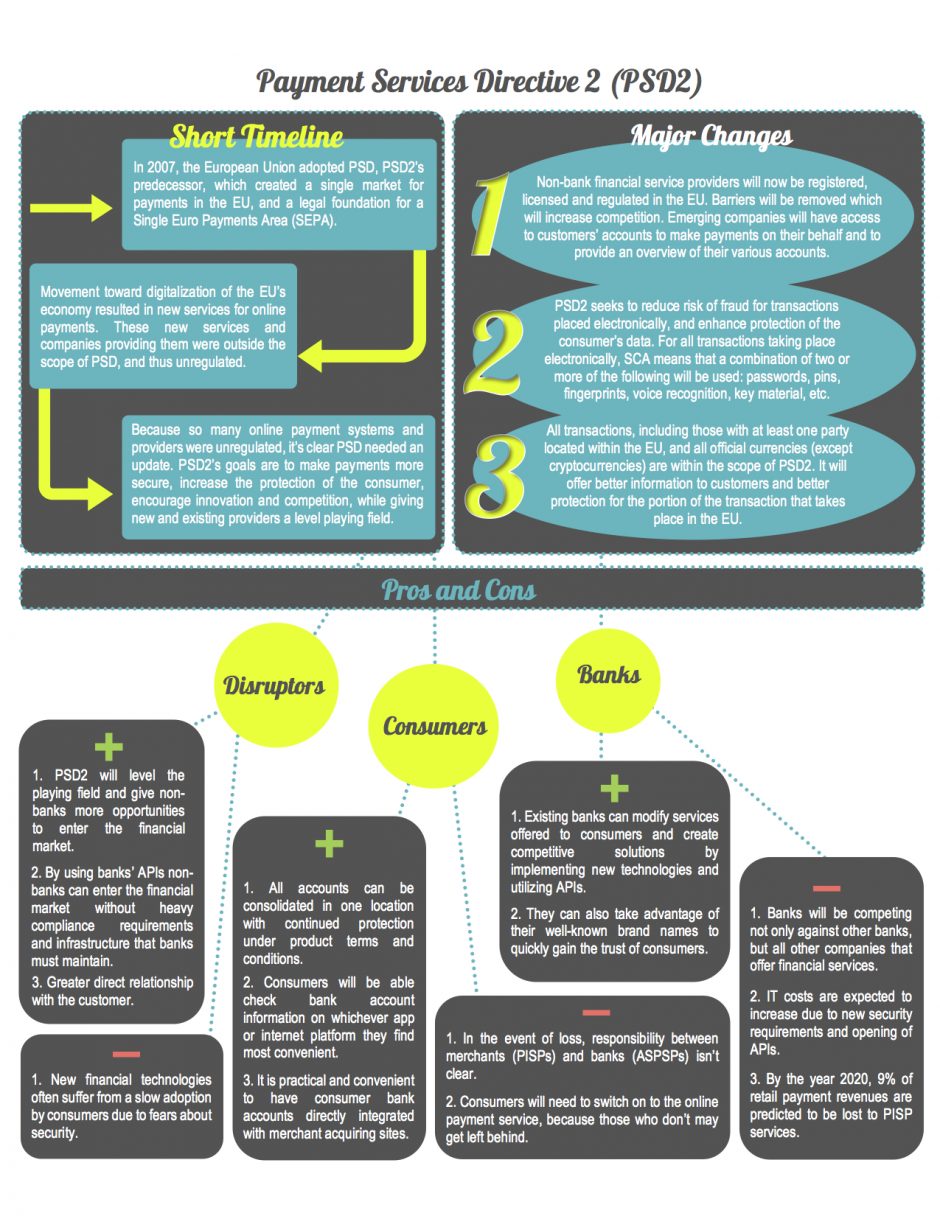
If you dont read anything else, this is your one-stop PSD2 infographic. It hits all of the key themes you need to know:
- Why the Payment Services Directive was created
- To enable the legal foundation of a Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA)
- The introduction and regulation of new financial services provided by newcomers
- Enabling safer payments, better protection for customers, driving innovation and competition
- The difference between PSD and PSD2
- Allowing newcomers to access customer accounts to make payments and provide account reporting
- Institutions holding the account need to provide newcomers access to the account using APIs – Application Programming Interface
- Customers will be better protected through the use of SCA – Strong Customer Authentication
- PSD2 has introduced some lovely acronyms:
- XS2A – Access to account
- SCA – Strong Customer Authentication
- TPP – Third Party Payment Service Providers
- PSU – Payment Service Users
- ASPSP – Account Servicing Payment Service Providers
- AISP – Account Information Service Providers
- PISP – Payment Initiation Service Providers
- PSD2 Timeline
Ref: PSD2 Explained | European Payments Council
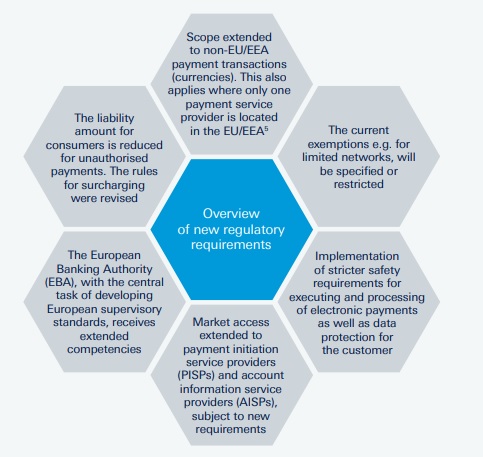
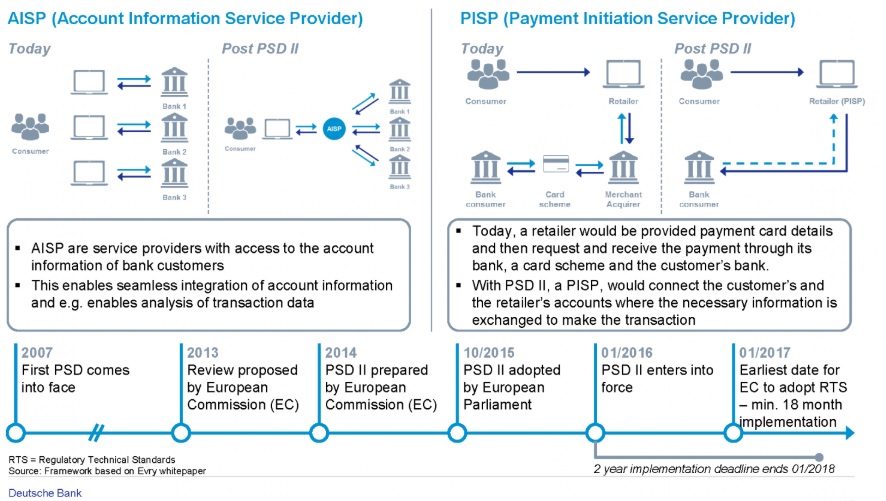
Key PSD2 Changes:
The following Deutsche Bank explanation indicates what PSD2 is, key changes include:
- Wider scope under PSD2
- Intra-EEA (European Economic Area) payments AND payments where the beneficiary or originator is outside of the EEA (One Leg Out Payments)
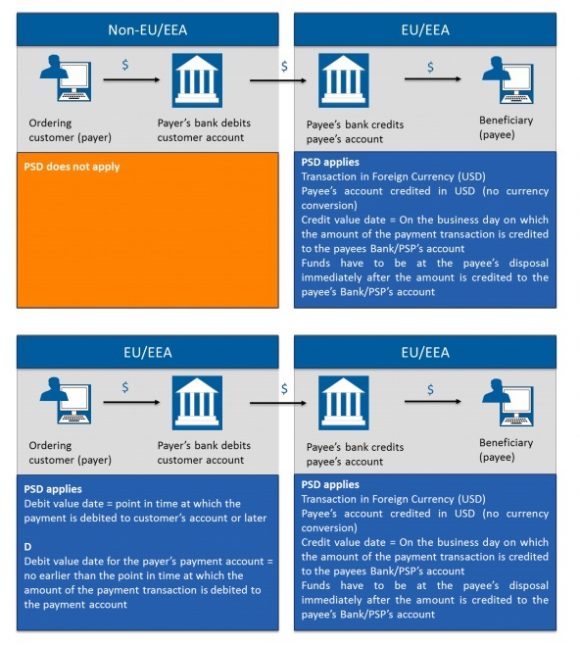
Source: Payment Services Directive (PSD2) | Tenemos
- Transaction Charges
- This where you need to understand the difference between transaction charge codes BEN, OUR and SHA
- In short, payments in currencies where the originator and beneficiary are both inside the EEA will use the charge option SHA

Source: Payment Services Directive 2 | Deutsche Bank
- Value Date
- For the payer (ordering customer) the Debit Value date is the date the bank receives the payment order (instruction to make a payment)
- For the payee (beneficiary), the Credit Value date is when the money is paid into Payee’s bank account
- Further customer protection
- The use of Strong Consumer Authentication, more on this below
- Introduction of regulated Third Party Payment Providers (TPPs)
- TPPs don’t hold customer account numbers themselves but where consent is provided serve customers as follows:
- PISPs – Payment Initiation Service Providers
- AISPs – Account Information Service Providers
- TPPs don’t hold customer account numbers themselves but where consent is provided serve customers as follows:
Ref: Payments Services Directive 2 | Deutsche Bank
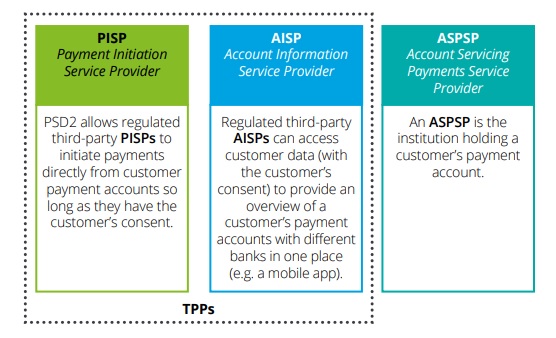
Whats the Difference between a TPP, PISP, AISP, APSP ?
Above we state what the acronyms mean, and this picture from the Deloitte whitepaper nicely indicates the key differences between the various institutions:
- ASPSP – Account Servicing Payment Service Providers
- The institution were the payment account is held
- AISP – Account Information Service Providers
- AISPs have the ability to access the customers account data
- PISP – Payment Initiation Service Providers
- With consent, these folks have the ability to initiate payments
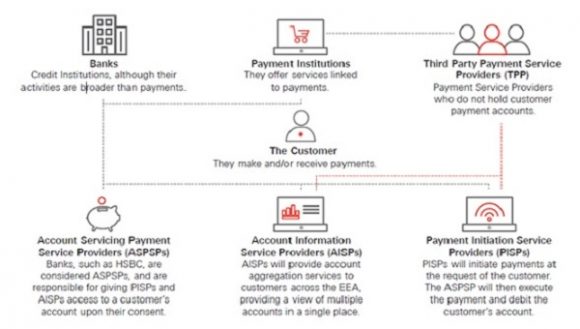
Source: Payment Services Directive II (PSD2) – Who is who | HSBC
This Deutsche Bank graphic focuses on the difference between a PISP and a AISP:
Ref: Payments Services Directive 2 | Deutsche Bank
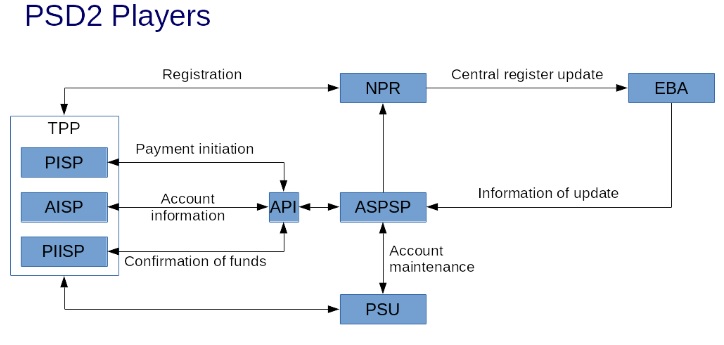
Who does what in PSD2?
Gabor Gazso does a great job of simply outlining Who’s who in PSD2.
Ref: Who’s who in PSD2 | Linkedin
PSD2 – The Pros and Cons – 8of9
This is a little wordy, but puts forward some PSD2 pros and cons:
- PSD2 Positive
- Enables newcomers to enter the financial services space and utilise bank developed APIs
- Levels the playing field across new and established players in the financial services space
- Facilitates better customer relationship
- All customer accounts can be managed in 1 place
- Innovation in payments enables established and newcomers to offer new services and solutions
- PSD2 Negative
- New fintech companies may experience slow adoption due to data privacy concerns
- If something between the PISP and ASPSPs goes wrong, we dont know who it responsible
- For banks, they are now competing with many companies, both in and outside of financial services sector
- It costs are likely to increase
Ref: PSD2 and Its Impact on Banking, Fintech and Consumers | 8of9
PSD2 to Implement RTS for SCA and CSC….. eh?
The above is saying that PSD2 will implement Regulatory Technical Standards for Strong Customer Authentication and Common and Secure open standards of Communication. The implementation of the Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS) is happening in September 2019.
Think:
- Security for when a customer:
- Accesses their account online
- Makes a electronic payment
- Does something online which triggers potential risk or fraud concerns
- Using Two Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Rules for when Strong Customer Authentication should and should not be used
- Access and how it is shared between the different PSD2 players
Ref: Understanding the Final Regulatory Technical Standards | European Payments Council
PSD2: The second Payment Services Directive – Sia Partners
The following infographic covers some of the same information, but with some notable additions:
- PSD2 Pillars:
- Processing operations
- Access to accounts
- Security and operational risk management
- A focus on innovation in the financial services industry, the growth of electronic payments driven by innovation leading to transformation in 2 ways:
- Compliance
- The need for financial institutions to offer APIs
- TPP access to account information (AISPs) and payment initiation (PISPs)
- Customer protection against fraud
- Better security
- Competition
- Become a AISP or PISP
- Enable a healthy ecosystem through Open Banking
- Creation of new services, products and APIs
- Take advantage of new business opportunities
- Compliance